ConfigPortal Staging [C OG]
Overview
Staging is a process to merge data from one repository to another. This allows to test configuration changes in one environment (e.g. an integration system) and take them afterword to another one (e.g. a production system).
ConfigPortal utilizes the merge functionality from Git to combine the data from the two repositories. Git keeps the snapshot of each data change, which makes it easier to review the changes from its history.
Staging is located at in the ConfigPortalUI → Setting → Staging. The Staging page is only visible only for users with the roles CP_EXPERT or CP_ARVATO applied.
ConfigPortal staging view
Once users download a state of ConfigPortal's configurations locally from the Info Page, they can then upload into the central server via the Staging Page. It is important to know that configuration states are always downloaded to the local repository before they can be uploaded. When performing the upload, the Staging Wizard guides one through the process of upload and the synchronization of data from different Staging Environments. In essence, the purpose behind Staging is to have functional configurations as identical to each other as possible, across the different Staging Environments. The closer they are to each other in terms of function configuration, the more accurate the analysis for troubleshooting and errors becomes. However, certain values are particular to a Staging Environment. These include parameters such as IP addresses, hostnames, web service endpoints and are handled differently during the Staging process. This is where a comprehensive review of the concept and process of ConfigPortal's Staging comes in. It is highly recommended that users performing change of this nature become acquainted with key concepts and benefits, well before attempting to perform the Staging process themselves.
Staging Methods
There are two options of to merge changes in the staging:
Full Merge - Include history
Partial Merge - Selective merging
Full Merge
The default merging option in ConfigPortal is the full merge. With this option, users can combine the commit histories of both the source and target repositories. Full merge is the recommended method for staging. Here are the benefits of using full merge:
Faster Subsequent Merging: When repositories have previously undergone merging, full merge speeds up subsequent merging. It does so by keeping track of the commit point where the two repositories where combined.
Comprehensive History: Full merge includes the history from both the target and source repositories. This makes it easier for users to diagnose actions such as deletion or modification of records.
Accurate Data Flow: By using full merge, changes to data are tracked more accurately across multiple environments.
Partial Merge / Selective Staging
This feature is available in CP 24.2 onward
Partial merge, also known as selective staging, allows users to perform partial staging by choosing the needed changes of data that need to merge into the target environment. It is similar with cherry-picking in Git merge. It lists out the changes between the source and target repository since the last full merge commit point. Users can then choose one or multiple pieces of data to merge into the target environment.
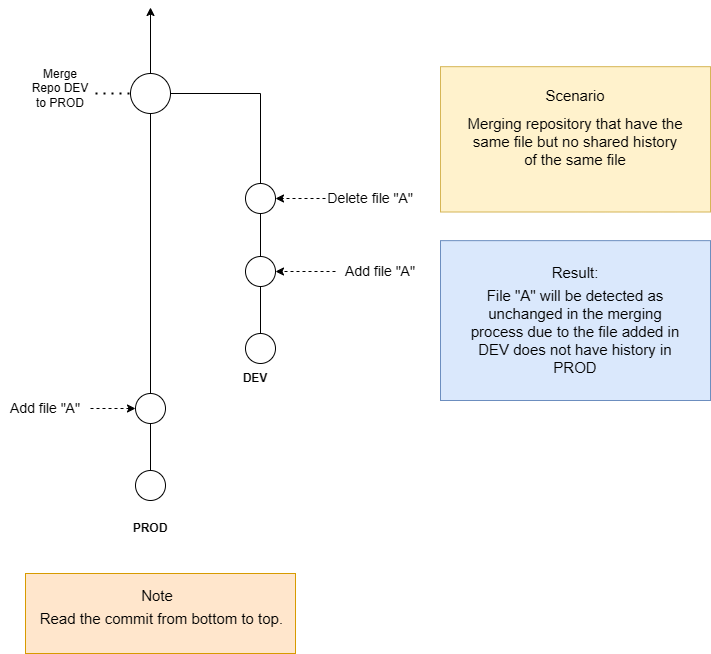
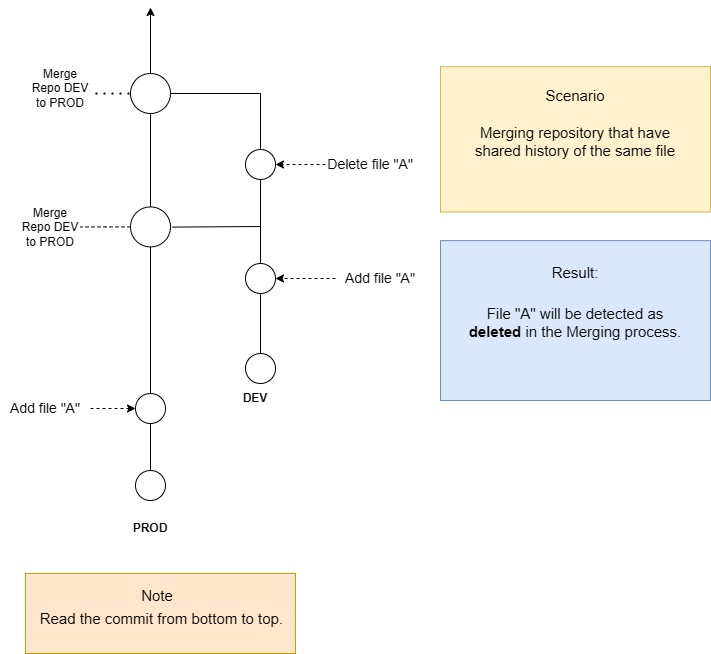
However, it is important to note that using partial merge does not merge the entire history of the source repository into the target repository. This means that if both environments contain the same data with different values, the subsequence staging action for that data may be overwritten or ignored from the source repository if there is no common commit history of same file detected.
Advantages of Partial Merge:
Selective Merging: Users can merge only the necessary data into the target environment, avoiding unnecessary changes.
Quick Testing: Partial merge is useful for quickly testing unique scenarios without affecting the entire data in the repository.
Risk of Partial Merge:
Deletion of a file in source environment might not be detected correctly and for that reason ignored in the target environment.
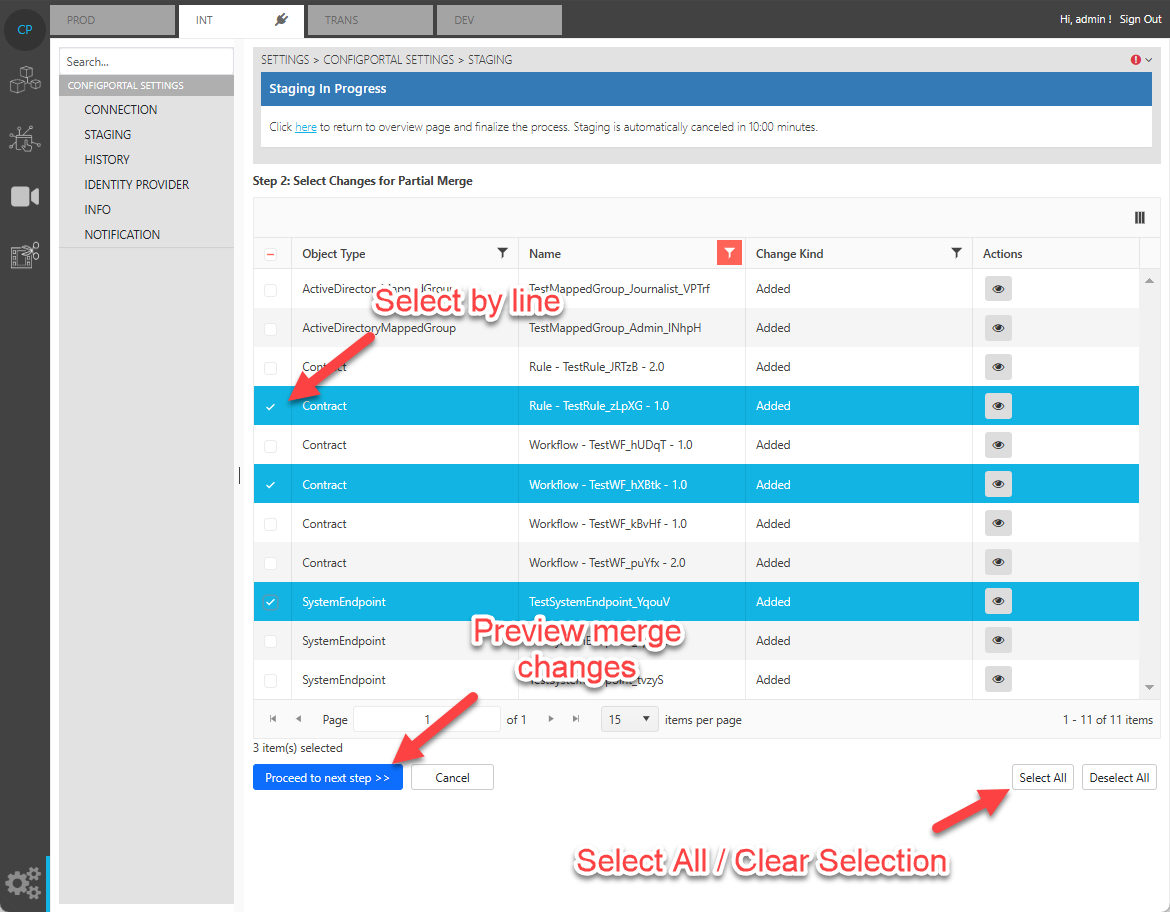
All the changes made during the selective partial staging “Step 2” process in ConfigPortal will be written into master. ConfigPortal will be switched to use staging data only in the preview step “Step 3”.
Enable Selective Staging
The selective staging option is disabled (hidden) by default, user can enable the option from the “Setting → Connection” page. Edit the “Active” Environment, and set the “Allow Selective Staging” option to true.
Do note that, this option is only recommended for none production environment.
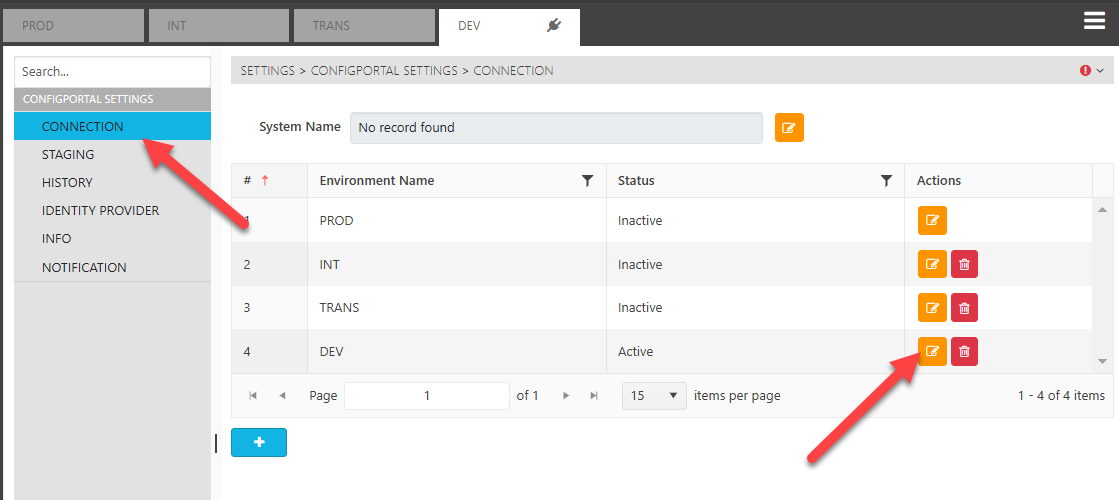
Connection Page
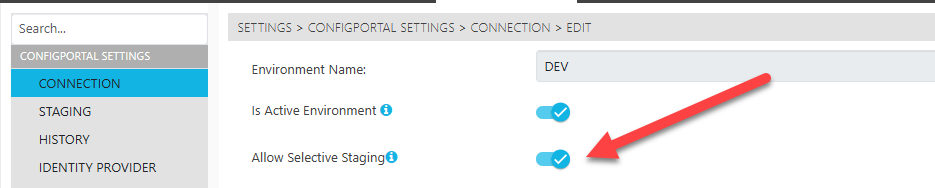
Allow Selective Staging Option
After update “Allow Selective Staging” to true. User shall able to find the “Partial Merge” in staging page.
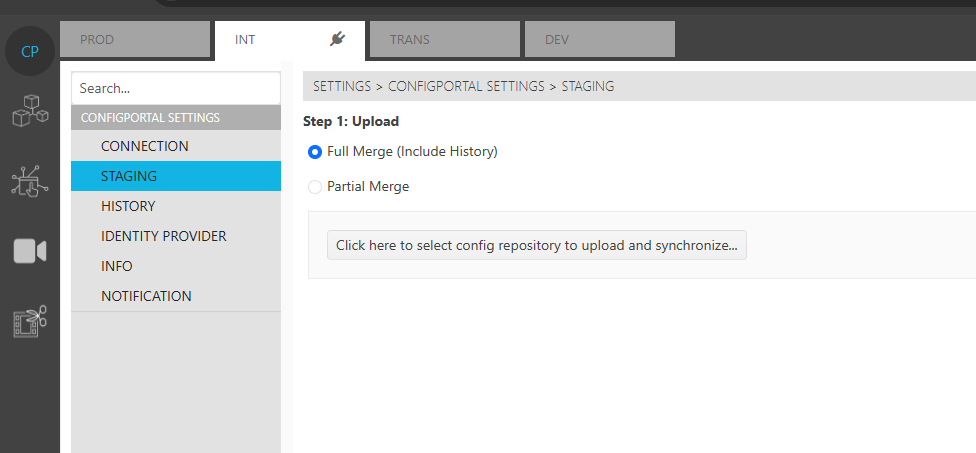
ConfigPortal staging view with partial merge option
Preview Staging
When staging data in ConfigPortal, it combines information from two repositories.
During this process, all changes made in ConfigPortal (such as reads, writes, or deletions) will use the staging data, not the master data. All the changes made during this process will be displayed in the staging overview page.
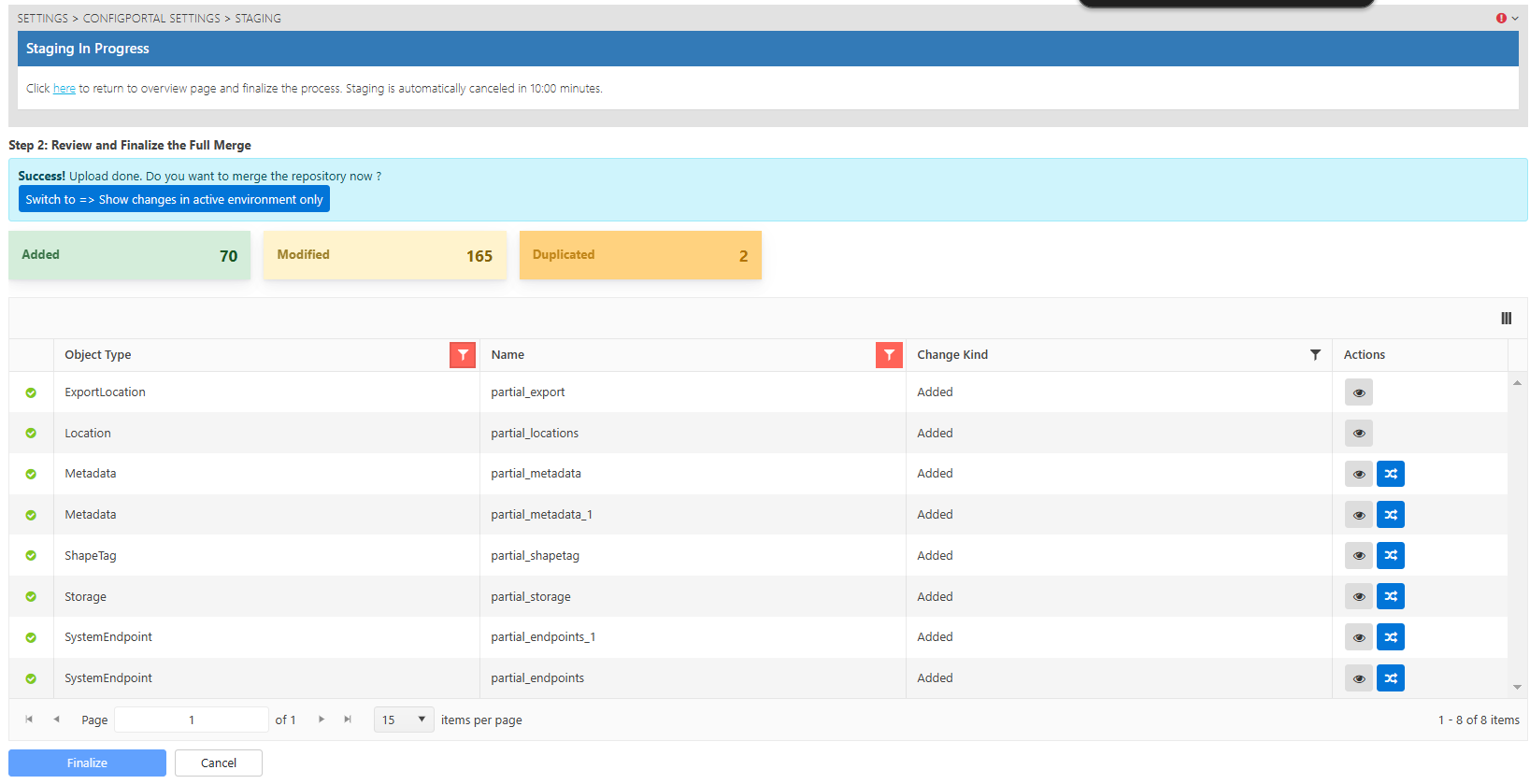
Users can click on the preview icon to check on the online and offline data before finalization.
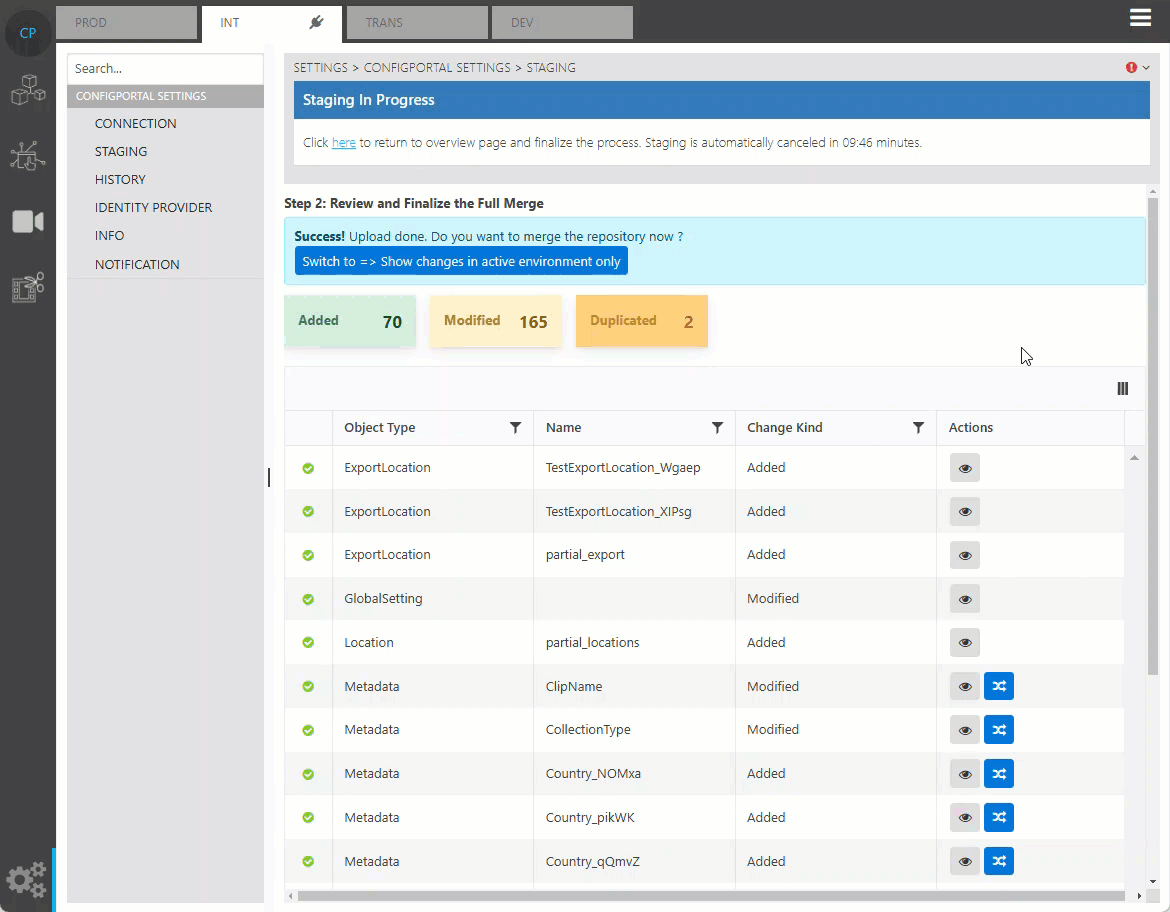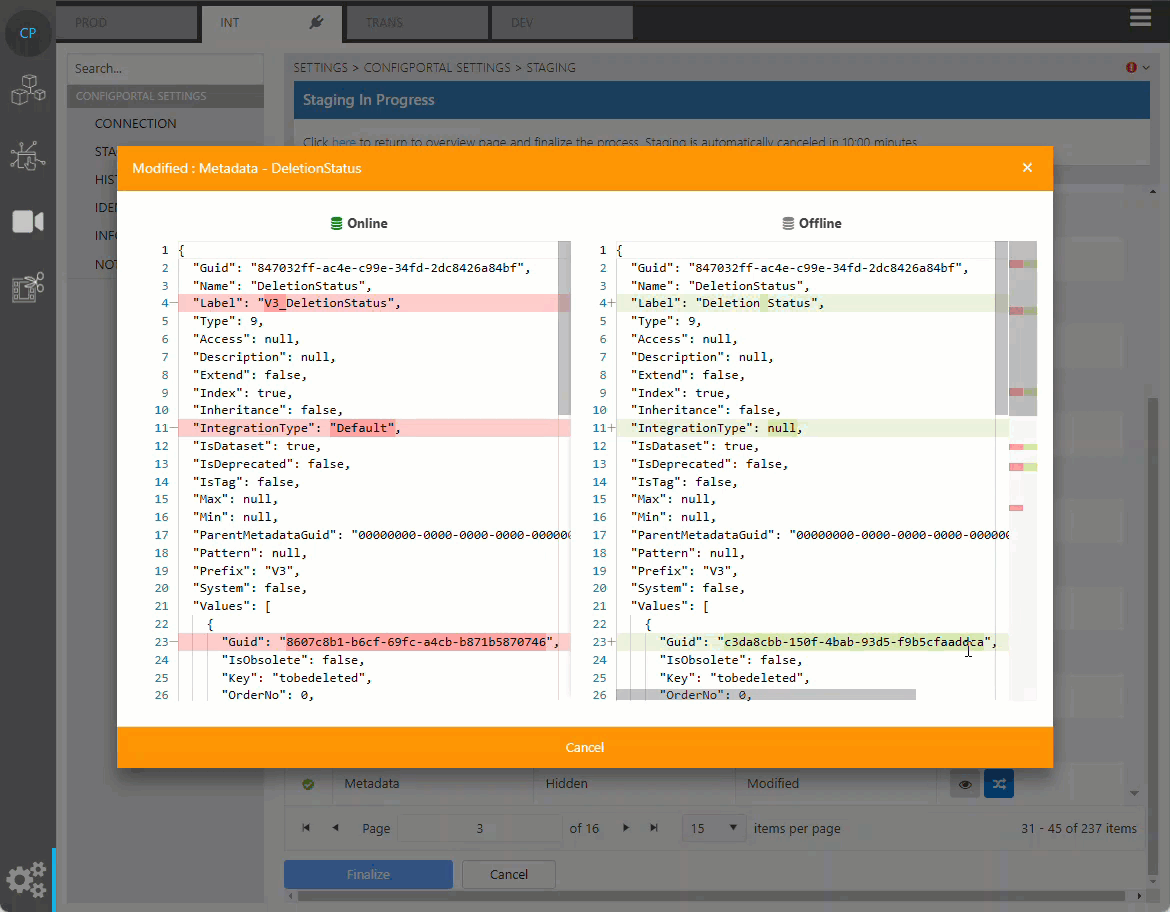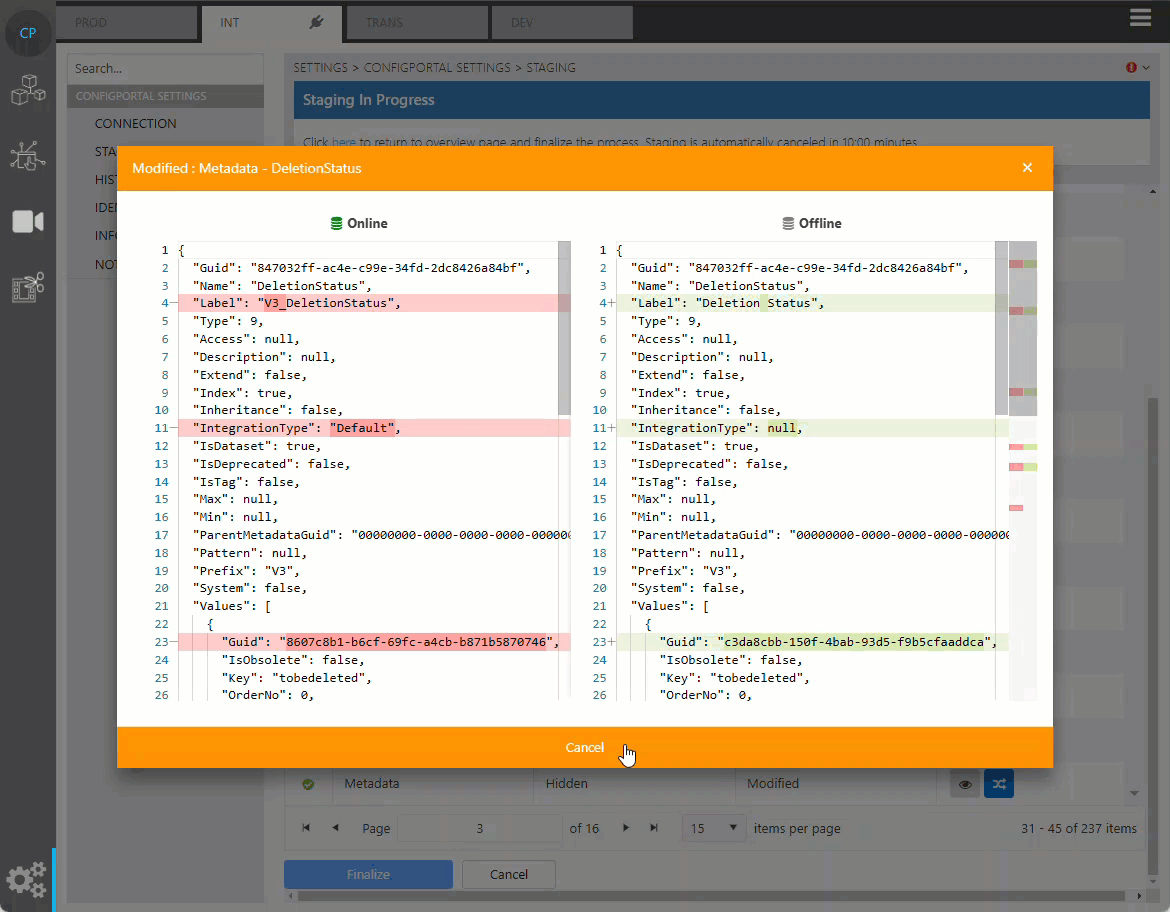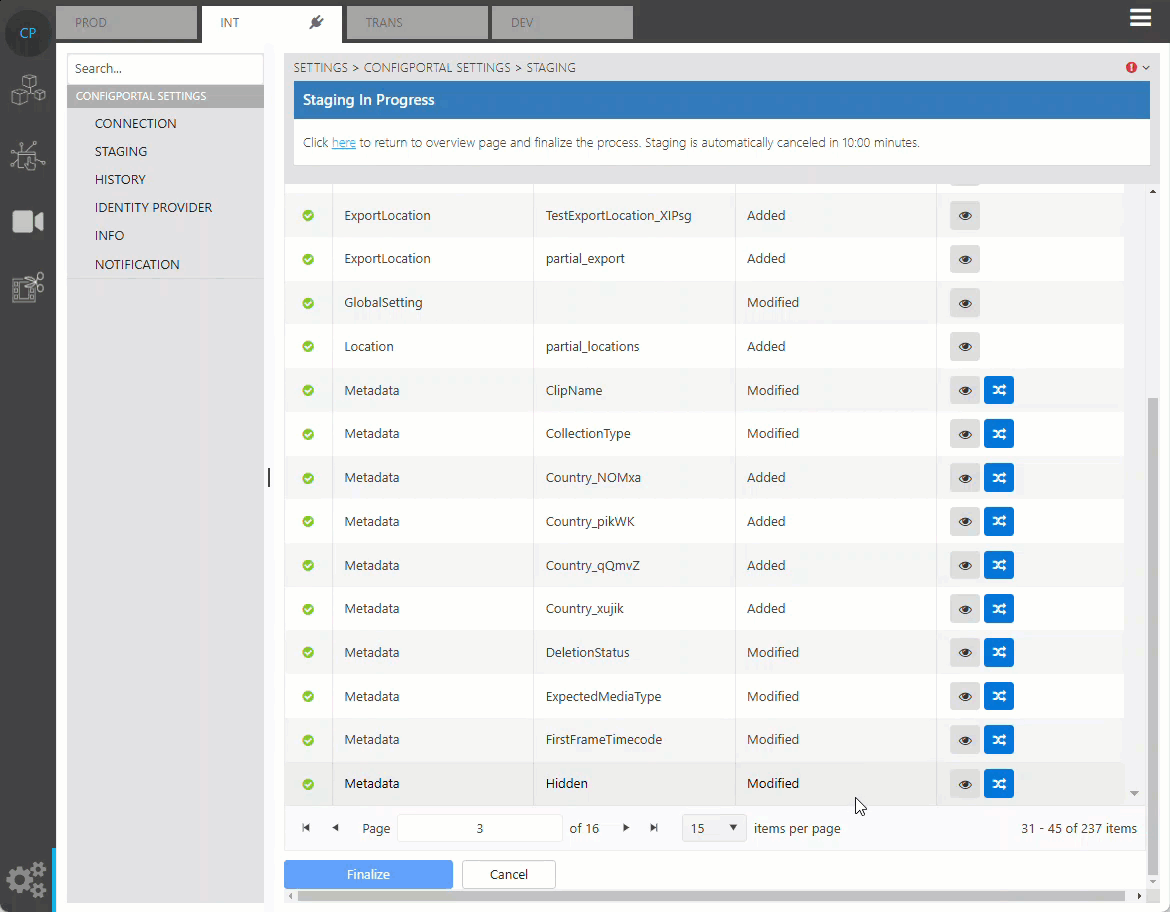
Review Merging Data
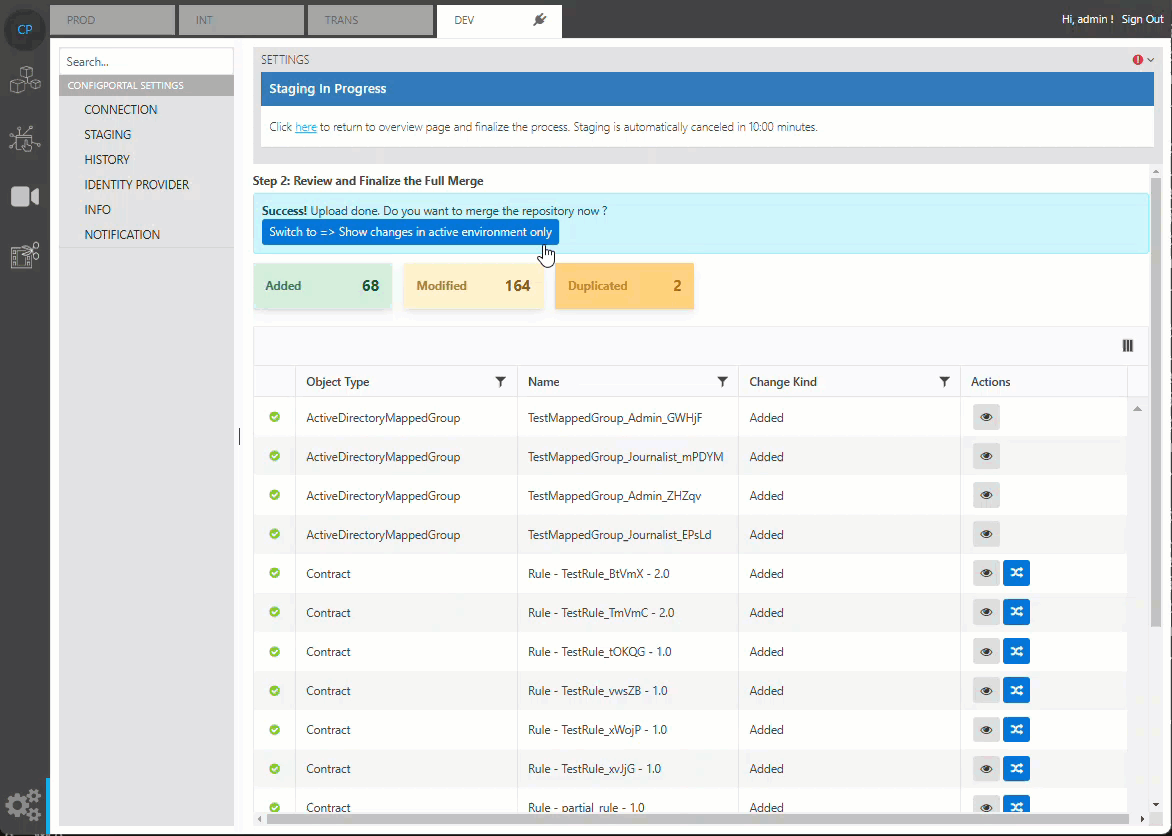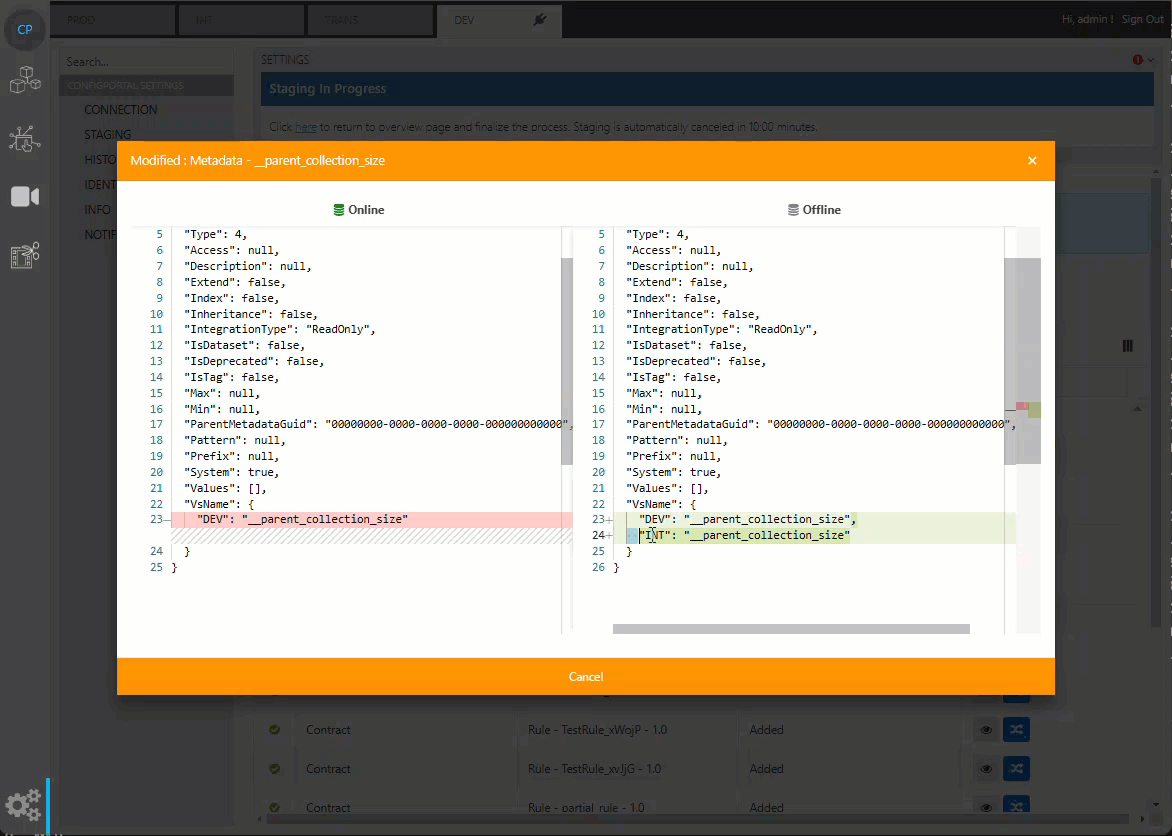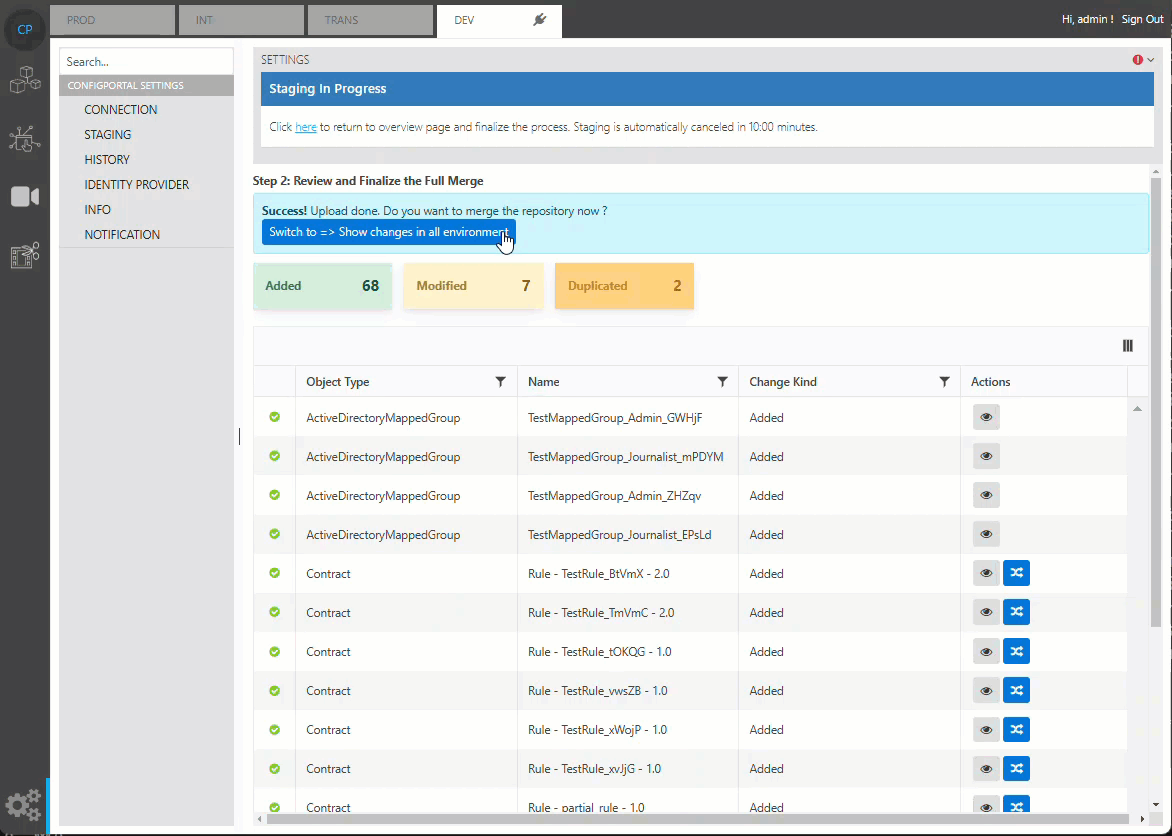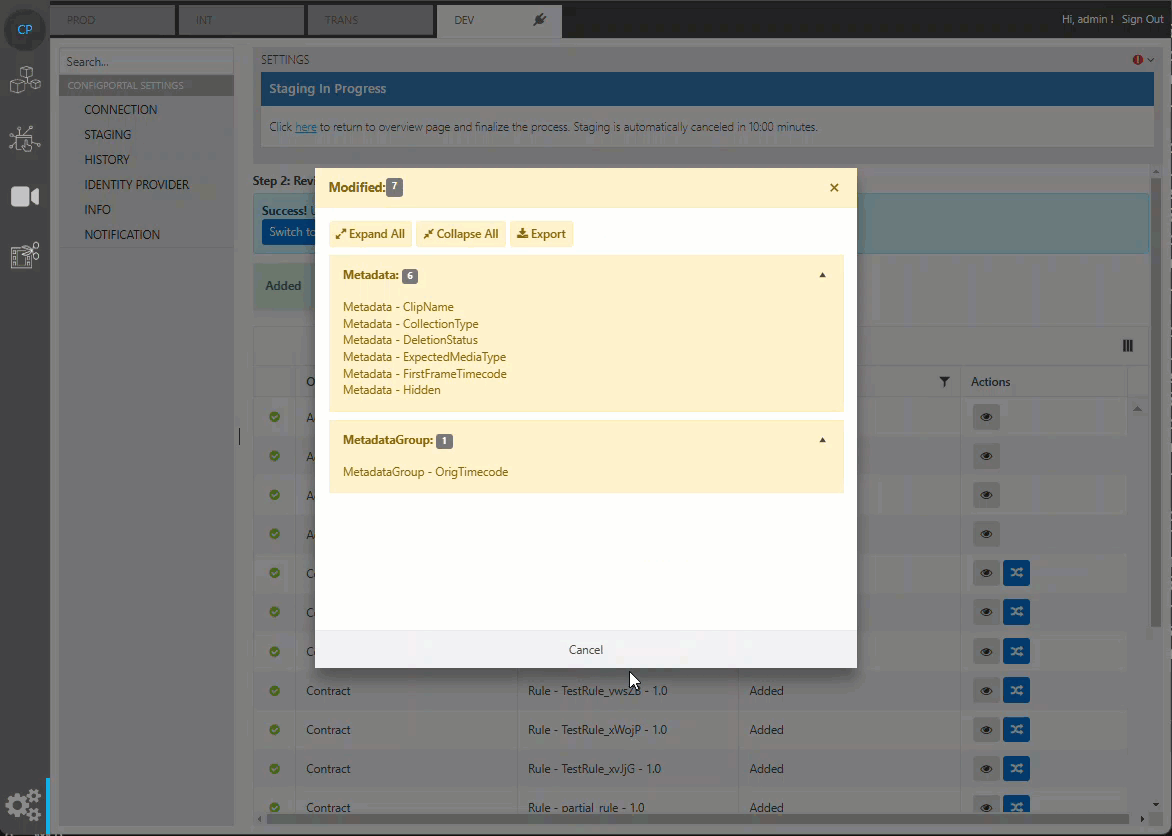
Show Changes in Active Environment
By default, ConfigPortal will show all changes between the source and target repository, which also includes all changes in environment data in the source repository. The ‘show changes in active environment’ option can be used to filter out changes only in the target environment, making it easier to review the changes that affect the target environment.
Fix Item With Validation Error
In cases where the staging overview shows a validation error for an object, even though it will still allow the user to complete the staging without fixing it.
It is always recommended to address the error before finalizing the staging!
In most of the cases, the validation is related to missing mandatory values in an environment value (e.g. the rootpath of an storage method may be missing).
To fix an item with a validation error, choosing the navigation button on the right hand side will navigate to the configuration page of this item, where it can edited directly. The modifications made at this step will be written to the staging data. It will be merged into the master data only when the button “Finalize” is triggered to execute the staging.
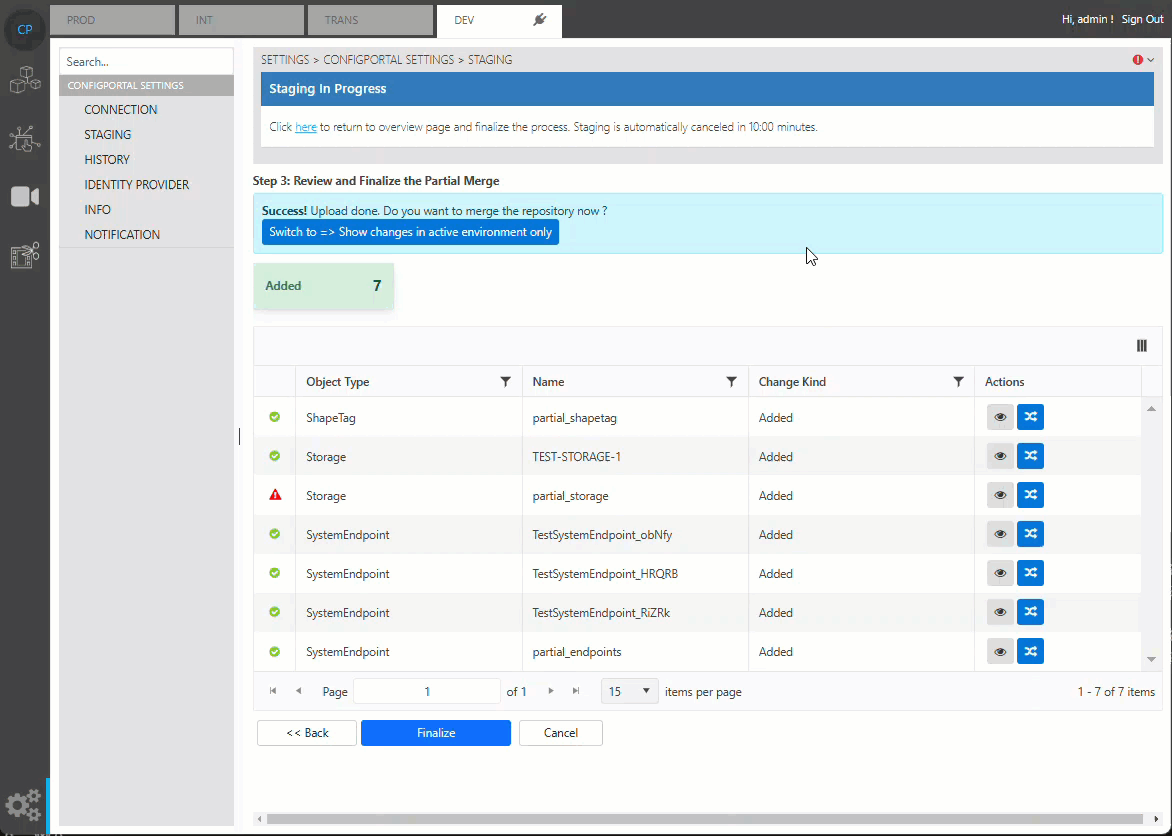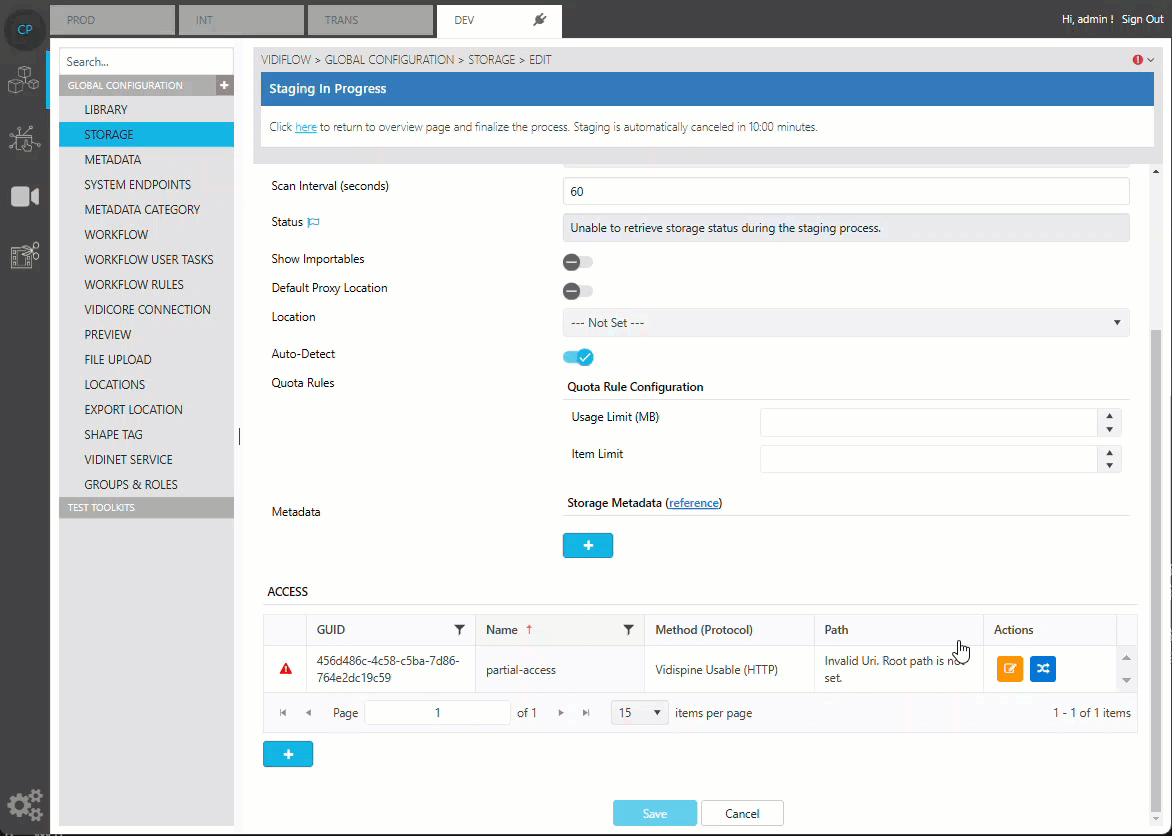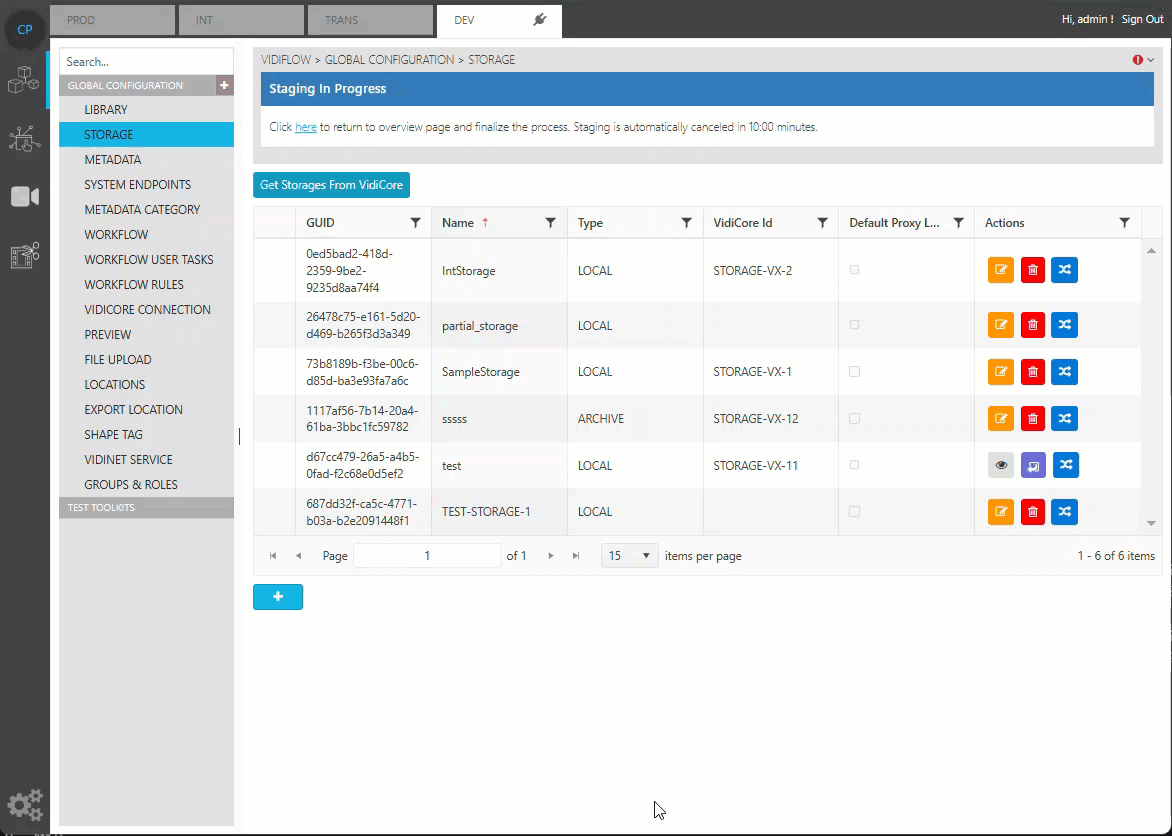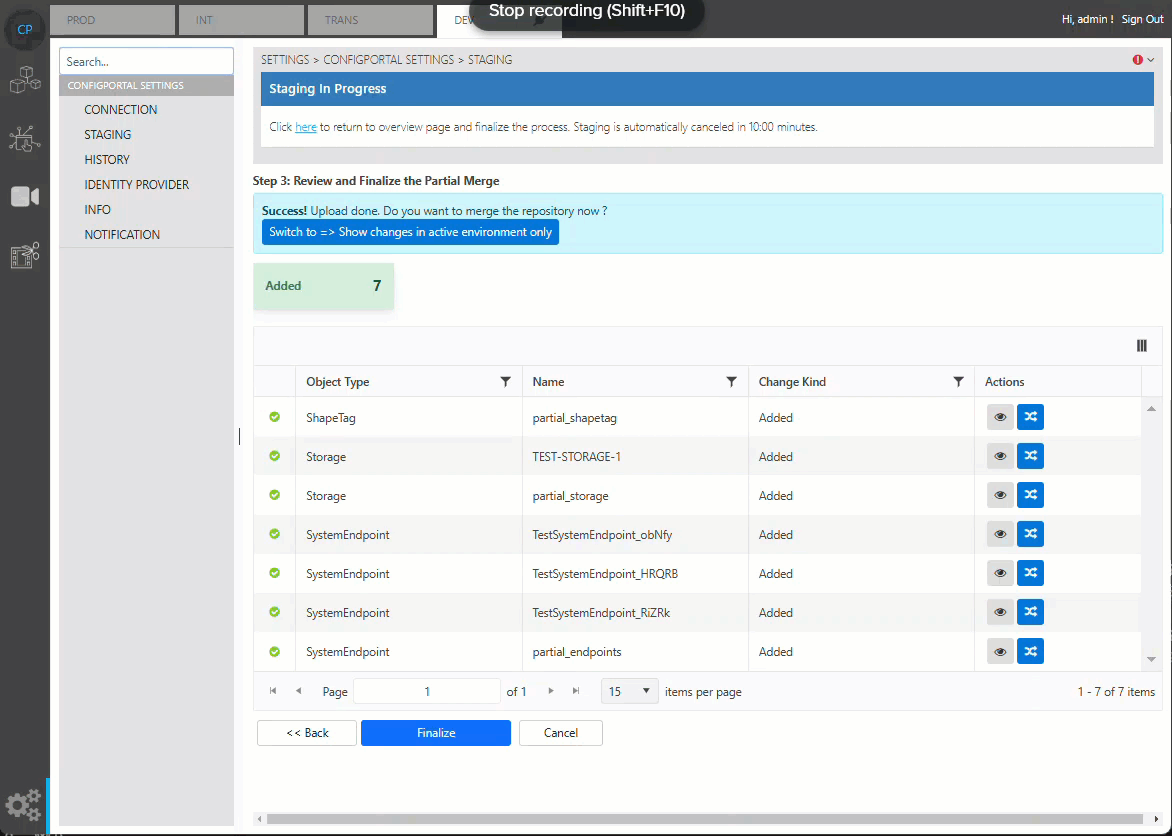
Fix missing values via the navigation button
Resolve Duplication
If duplication of data detected, ConfigPortal will not allow the user to complete the staging until the duplication is resolved manually. This can be done from the preview data dialog. Either the online or offline data can be chosen to be kept in the target repository.
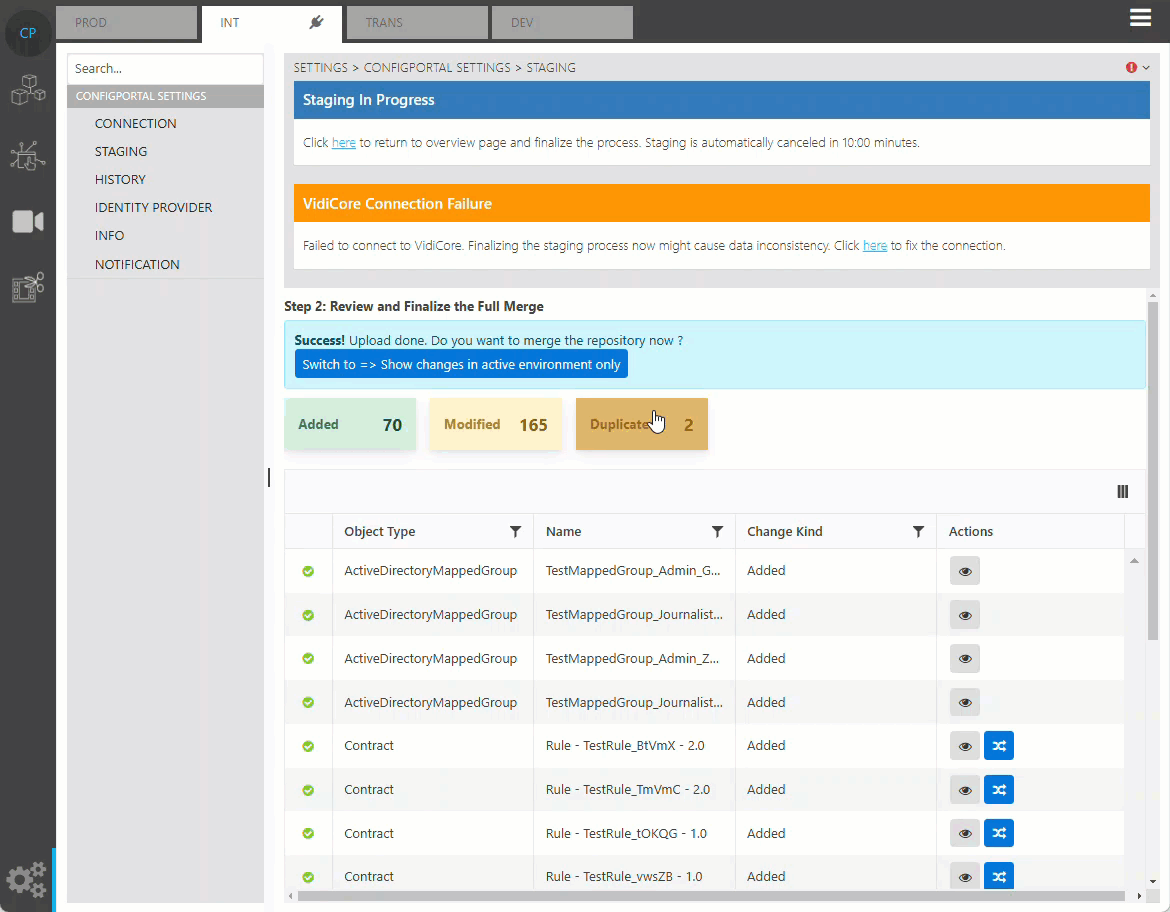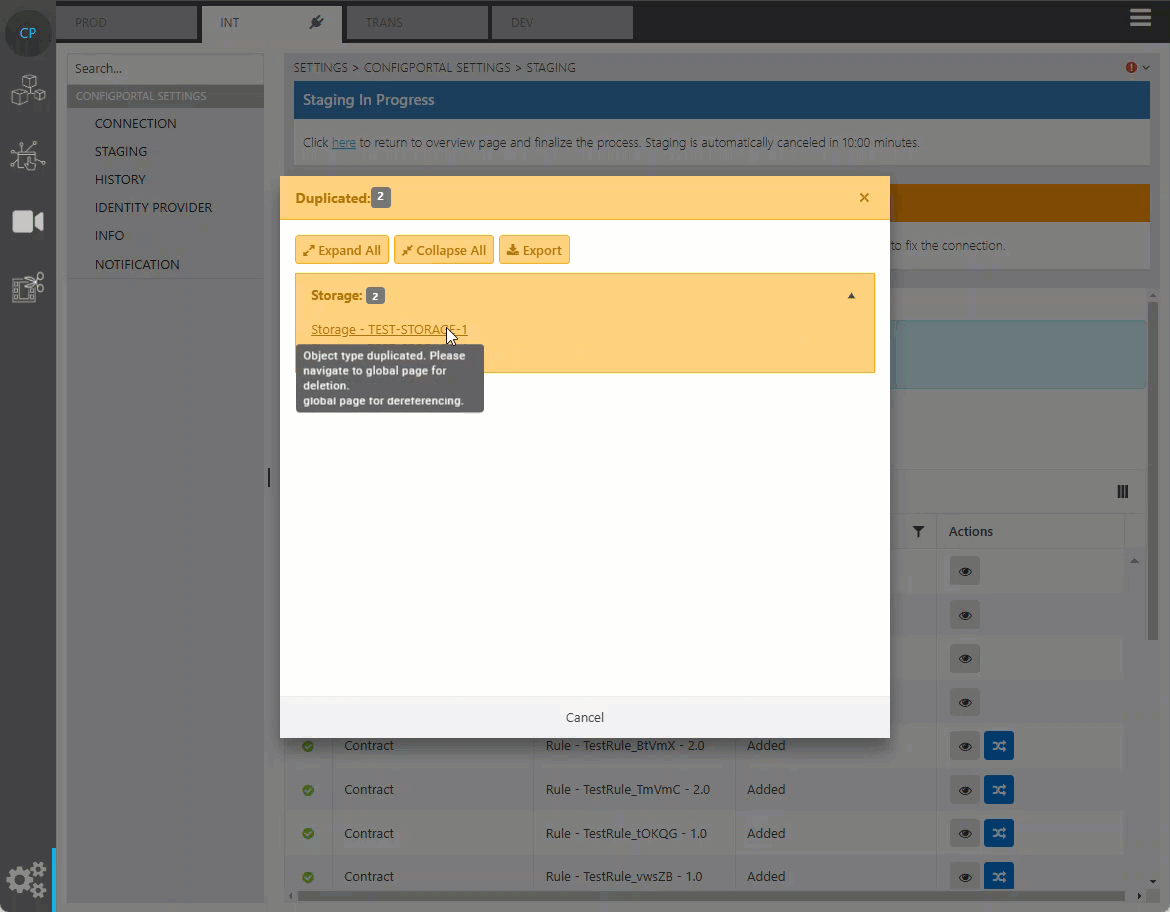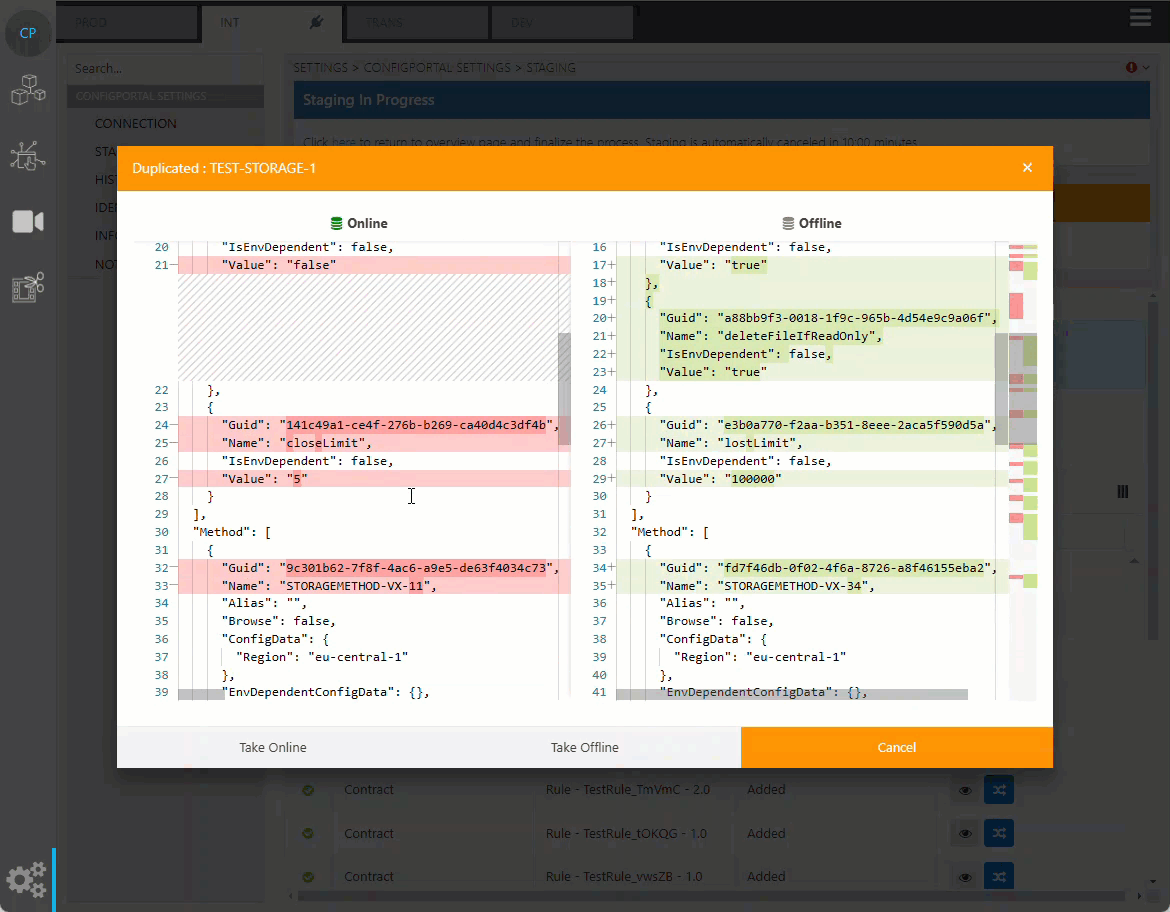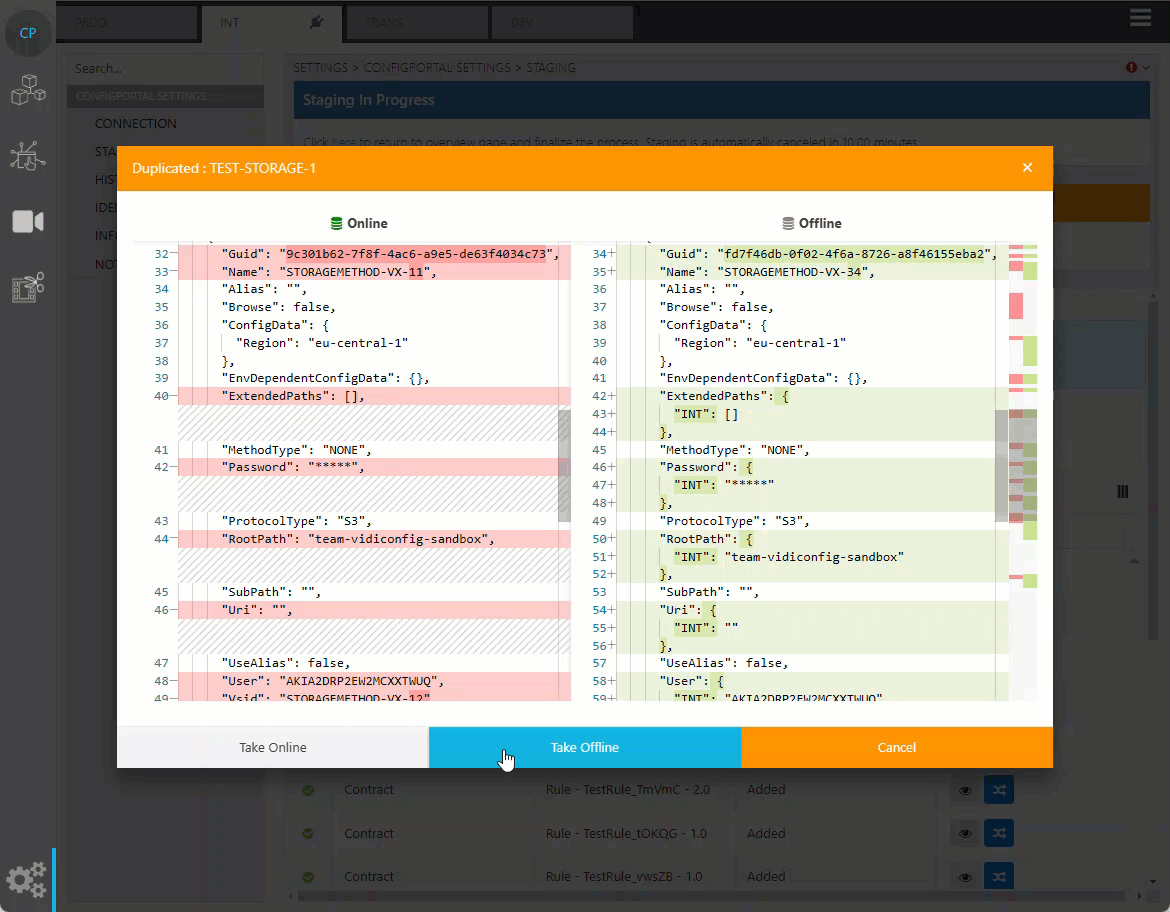
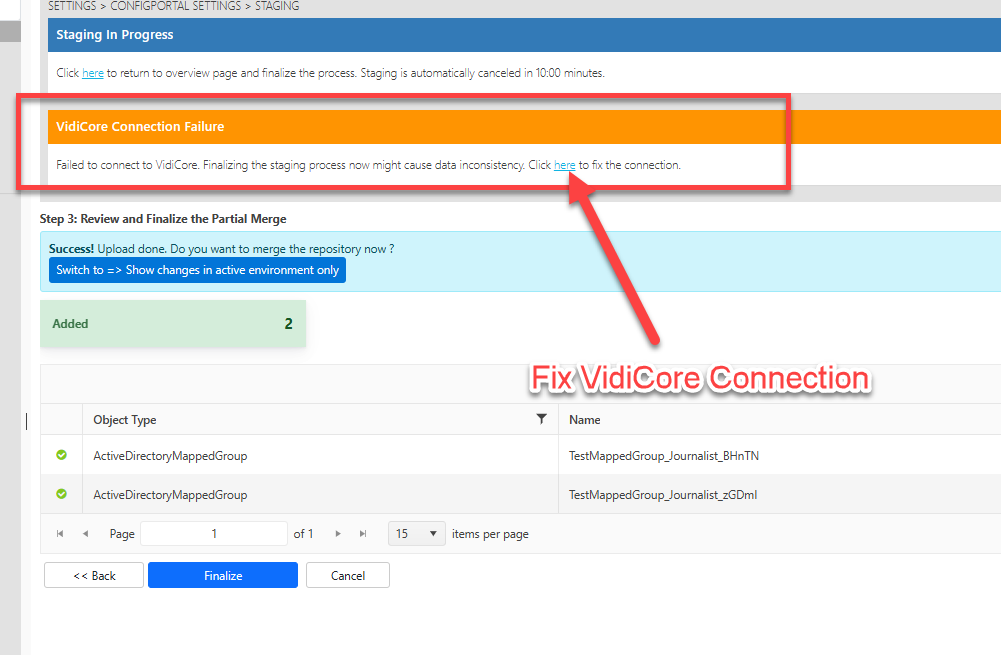
Vidispine Connection Failure
If there is warning “VidiCore Connection Failure” shown on top of the the staging page, it has to be made sure the connection to VidiCore is correctly configured before finalization of the staging. This is important because many aspects of the staged data will be synced into VidiCore upon the finalization of the staging process.
Export Data
To export a single data item, open the data preview dialog and look for the download icon.
Starting from CP Version 24.3, the preview dialog will not display data that is too large. In such cases, the export feature allows users to export the raw data, including the full data.
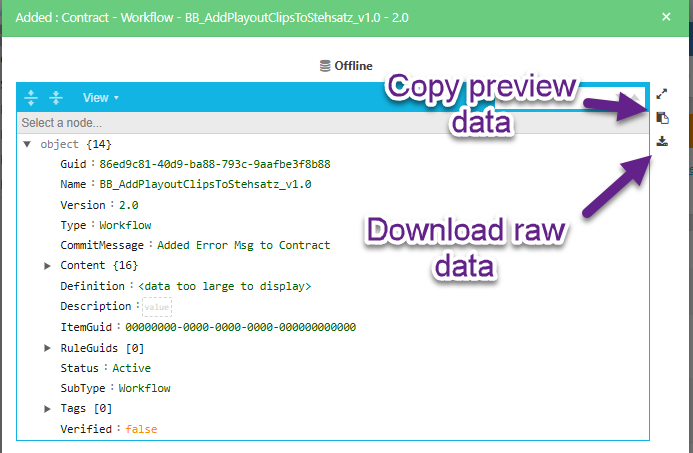
The copy icon in the dialog will only copy what is shown in the preview dialog, while the download button will retrieve the full raw data for the selected staging data.
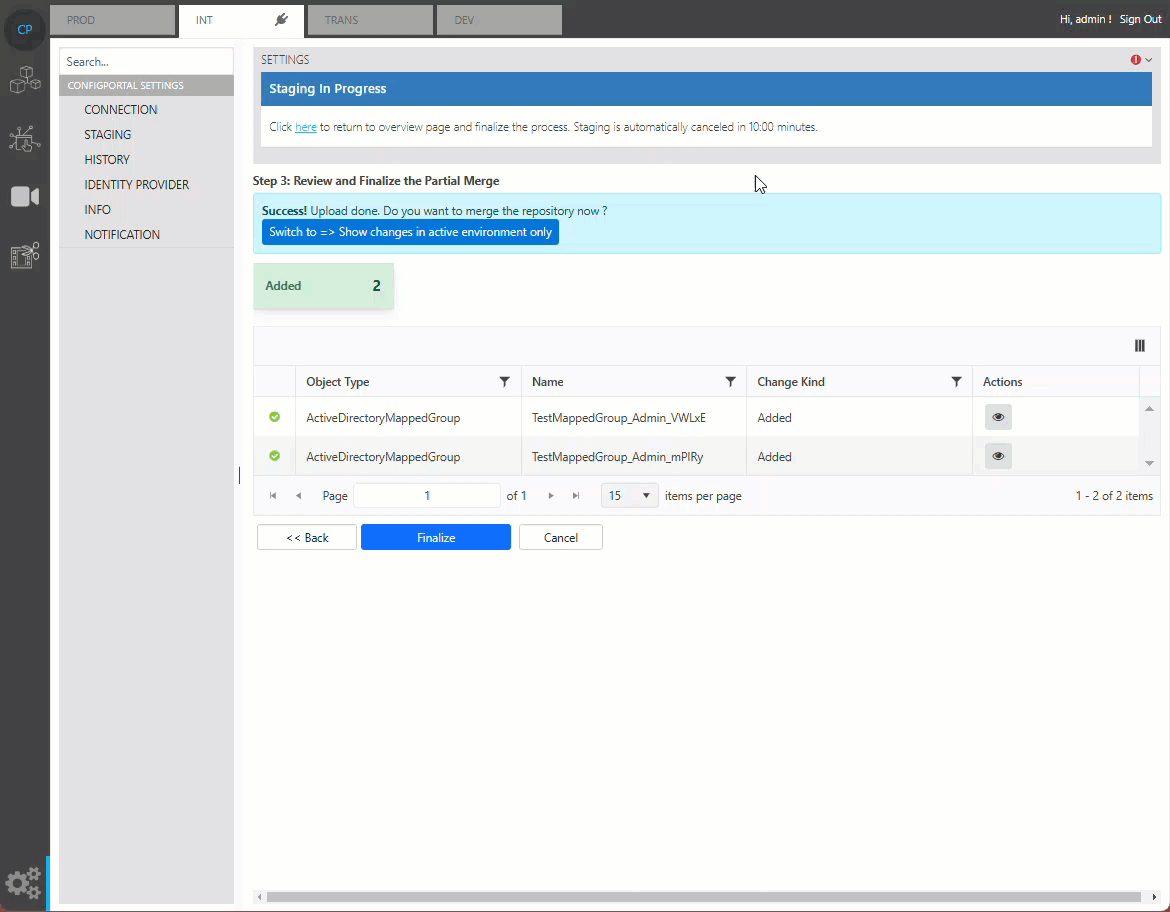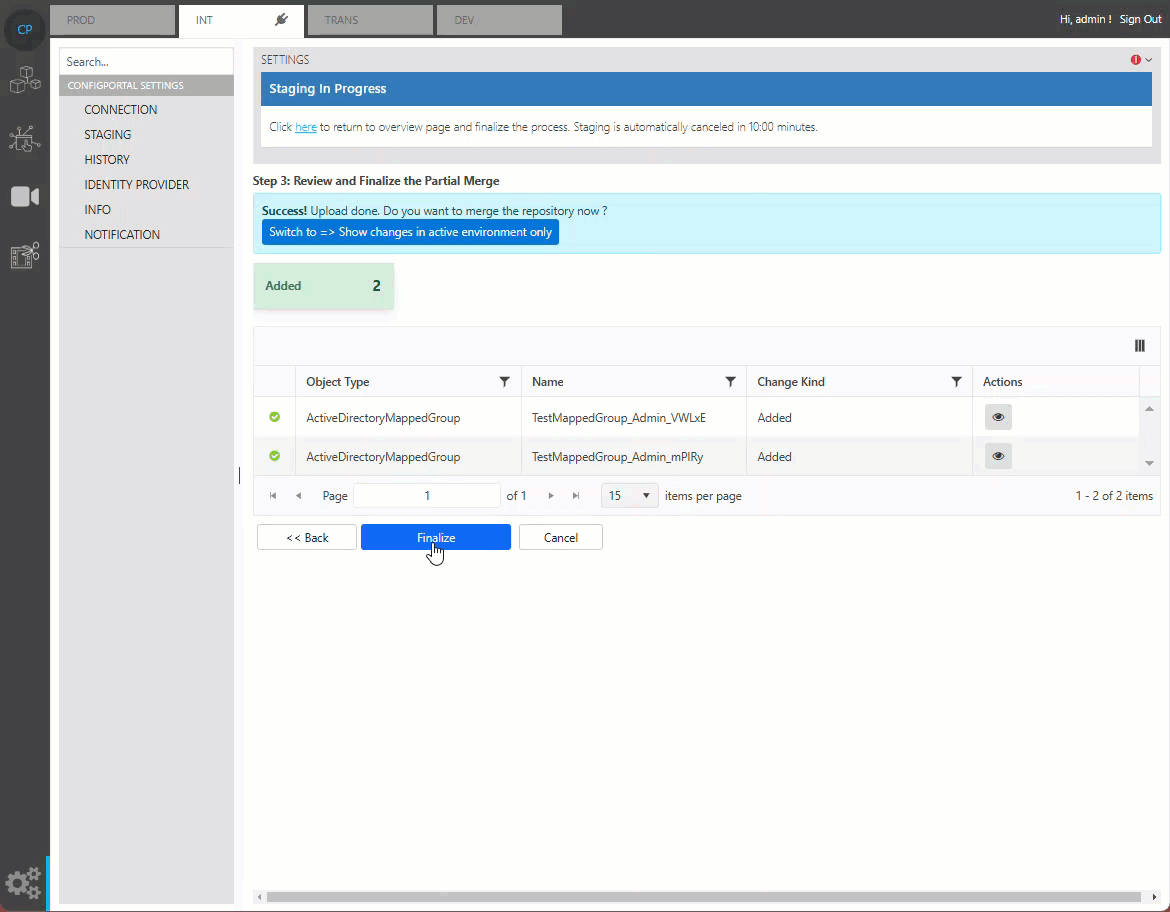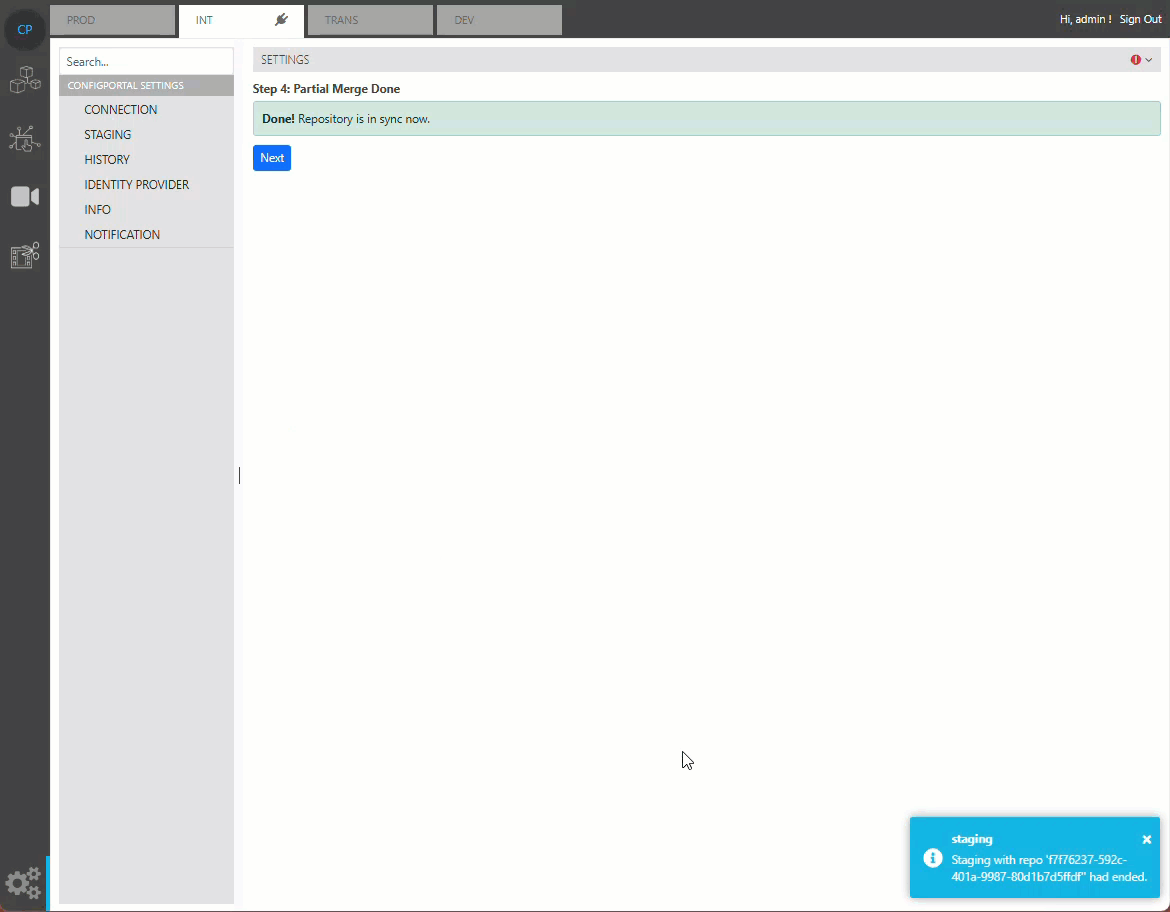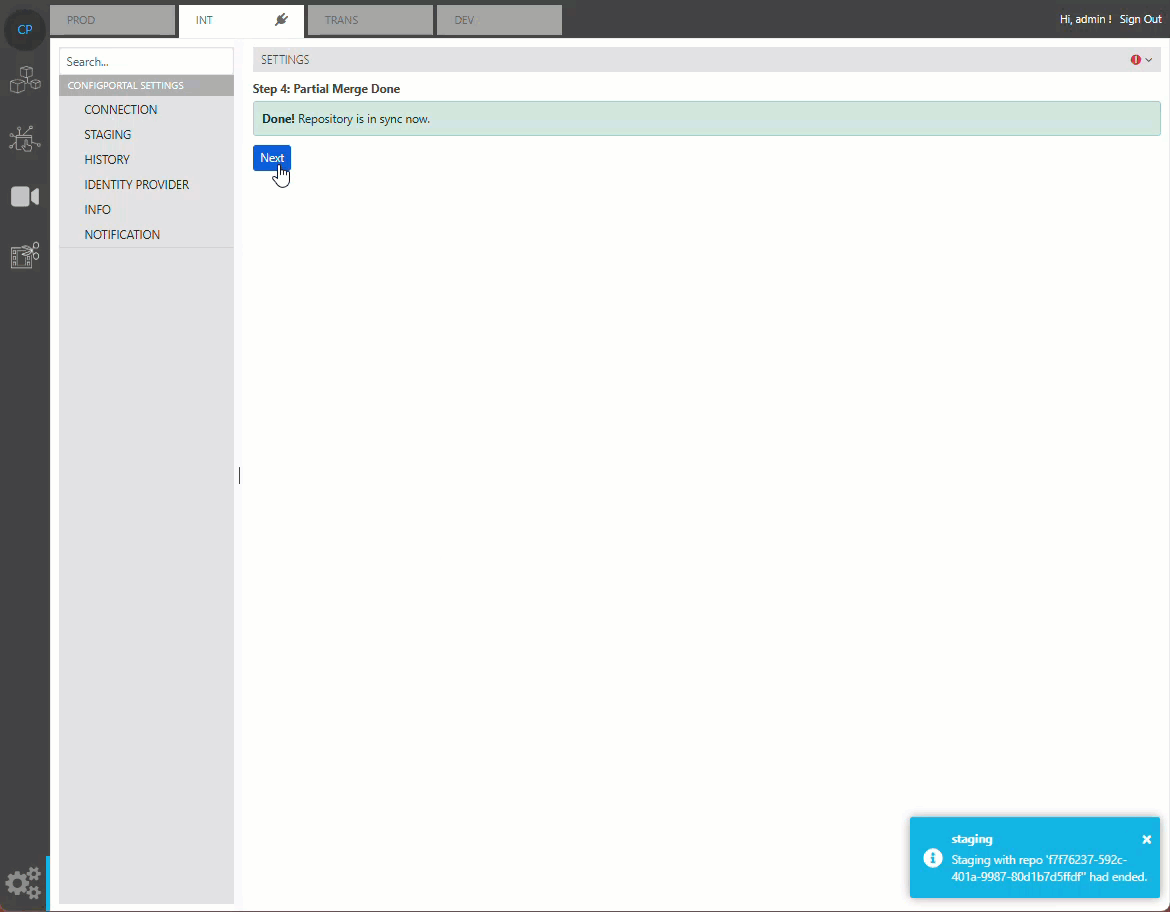
Finalizing Merge
Once all changes are confirmed, user can complete the staging by pressing the finalization button. This will merge the staging data into the master data.
Finalizing staging
FAQ
Why is some data that was deleted in the source environment not shown as deleted in the target environment?
Scenario: An item (e.g. Workflow Contract) with same name and version added in both target and source environment separately. The item gets deleted in source environment afterward.
Question: Will the item showed as deleted in the target environment during the staging?
Answer: If the item do not have shared history, staging will ignore the deleted item from source, and keep the item in target environment unchanged. If the item have shared history (eg, full merge done previously), it will detect the file as deleted in the staging process.
Diagram: File deleted in source without shared history
Diagram: File deleted in source with shared history